Bootstrap Navbar Working
Introduction
Despite of how tricky and well-thought site organization we produce, it doesn't mean a great deal if we do not give the end user a practical and easy-to-use way accessing it and getting to the specific webpage needed rapidly and with least efforts no matter the screen size of the device displaying the website. If it goes to responsive behavior, the navbar can be set up to collapse under a specific screen width and a screen horizontal above it looks and user sense. Here is exactly how:
Effective ways to apply the Bootstrap Navbar Working:
Here's the things you require to know right before getting started along with the navbar:
- Navbars need a wrapping .navbar with .navbar-toggleable-* to get responsive collapsing as well as color arrangement classes.
- Navbars and their materials are adjustable by default. Utilize optionally available containers to limit their horizontal width.
- Navbars as well as their materials are developed by using flexbox, providing quick and easy positioning alternatives with utility classes.
- Navbars are certainly responsive by default, but you can simply modify them to improve that. Responsive behavior depends on Collapse JavaScript plugin.
- Establish access utilizing a <nav> element or, if utilizing a much more universal component just like a <div>, add a role="navigation" to each and every Bootstrap Navbar Button to clearly determine it like a milestone location for users of assistive technologies.
We need a <nav> aspect to wrap the whole point up - designate it the . navbar class to start, a .navbar-fixed-top in order to have it stick at the top of the page whatsoever times or .navbar-fixed-bottom if for a factor you would want it fixed at the bottom. Here likewise is the area to look after the whole element's color-- in Bootstrap 4 you have some brand-new trendy clesses for that like .navbar-dark, .navbar-light or the classes connecting the history to the contextual colors in the framework-- like .bg-info, .bg-success and more. Certainly usually you might have a predefined color scheme to comply with - like a brand name's shade or something-- after that simply include a straightforward style =" background-color: ~ your color ~" feature or specify a bg-* class and also appoint it to the <nav> element.
If you want the navbar to collapse at a specified screen width here additionally is the place to use a button component with the classes .navbar-toggler and
.hidden- ~ the final sizing you would want the navbar showed inline ~ -up also adding the type="button" data-toggle="collapse" and data-target="# ~ the ID of the component holding the actual navbar content ~" - we'll get to this last one in just a moment. Since the flexible behavior it the significance of the Bootstrap framework we'll focus on producing responsive navbars because practically these are the ones we'll mostly require.
Statin things by doing this the next step in designing the navbar is producing a <div> element to keep the entire navbar and its items and collapse at the required screen size-- assign it the .collapse class and .navbar-toggleable- ~ the largest screen size where you want it collapsed ~ for example - .navbar-toggleable-sm
Within this element, you may optionally include a wrapper by having the .navbar-brand to share certain information about the master of the site and also the important navbar part-- the one storing the menu construction of your web site. It has to be wrapped in an unordered list or <ul> holding the .nav and also .navbar-nav classes. The <li> elements inside it need to be assigned the .nav-item class and the actual links in them - .nav-link class.
One other detail to keep in mind
A detail to note is that in the fresh Bootstrap 4 framework the methods of assigning the alignment of the navbar items has been changed a bit in order various appearances to be possibly assigned to different screen sizes.
You can at last make a decision to put a simple form part inside your navbar-- usually right after the .nav element. To make it display correctly you can make use of the positioning classes discussed above also assigning .form-inline to it. The .navbar-form class the forms needed to carry in the previous version has been dropped in Bootsrtap 4.
Continue reading to get an instance and list of upheld sub-components.
Representations
Assisted content
Navbars included built-in service for a selection of sub-components. Select from the following as needed to have:
.navbar-brand for your company, project, or product name.
.navbar-nav for a light-weight as well as full-height navigating (including support for dropdowns)..
.navbar-toggler for use with collapse plugin and some other navigating toggling activities.
.form-inline for any sort of form controls as well as activities.
.navbar-text for including vertically structured strings of content.
.collapse.navbar-collapse for getting together and hiding navbar materials by a parent breakpoint.
Here is actually an example of all the sub-components included within a responsive light-themed navbar which instantly collapses at the md (medium) breakpoint.

<nav class="navbar navbar-toggleable-md navbar-light bg-faded">
<button class="navbar-toggler navbar-toggler-right" type="button" data-toggle="collapse" data-target="#navbarSupportedContent" aria-controls="navbarSupportedContent" aria-expanded="false" aria-label="Toggle navigation">
<span class="navbar-toggler-icon"></span>
</button>
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">Navbar</a>
<div class="collapse navbar-collapse" id="navbarSupportedContent">
<ul class="navbar-nav mr-auto">
<li class="nav-item active">
<a class="nav-link" href="#">Home <span class="sr-only">(current)</span></a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#">Link</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link disabled" href="#">Disabled</a>
</li>
</ul>
<form class="form-inline my-2 my-lg-0">
<input class="form-control mr-sm-2" type="text" placeholder="Search">
<button class="btn btn-outline-success my-2 my-sm-0" type="submit">Search</button>
</form>
</div>
</nav>Label
The .navbar-brand can absolutely be applied to most elements, and yet an anchor functions most ideal since a number of aspects might just require utility classes or customized formats.

<!-- As a link -->
<nav class="navbar navbar-light bg-faded">
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">Navbar</a>
</nav>
<!-- As a heading -->
<nav class="navbar navbar-light bg-faded">
<h1 class="navbar-brand mb-0">Navbar</h1>
</nav>Putting in pics to the .navbar-brand will very likely typically require custom-made styles or utilities to appropriately dimension. Here are some examples to indicate.

<!-- Just an image -->
<nav class="navbar navbar-light bg-faded">
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">
<div class="img"><img src="/assets/brand/bootstrap-solid.svg" width="30" height="30" alt=""></div>
</a>
</nav>
<!-- Image and text -->
<nav class="navbar navbar-light bg-faded">
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">
<div class="img"><img src="/assets/brand/bootstrap-solid.svg" width="30" height="30" class="d-inline-block align-top" alt=""></div>
Bootstrap
</a>
</nav>Nav
Navbar site navigation urls founded on .nav selections with their personal modifier class and require utilize toggler classes for correct responsive styling . Navigation in navbars will as well grow to possess as much horizontal area as available to keep your navbar components safely and securely lined up.
Active forms-- with .active-- to signify the existing webpage can be utilized right to .nav-link-s or their immediate parent .nav-item-s.
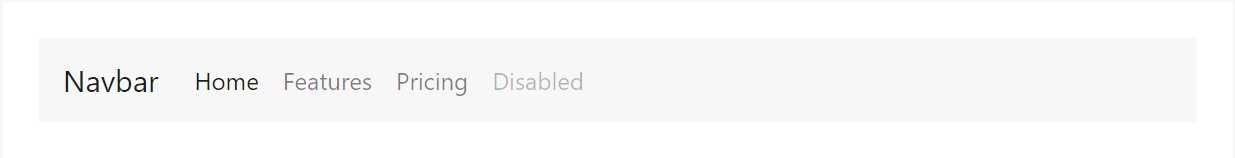
<nav class="navbar navbar-toggleable-md navbar-light bg-faded">
<button class="navbar-toggler navbar-toggler-right" type="button" data-toggle="collapse" data-target="#navbarNav" aria-controls="navbarNav" aria-expanded="false" aria-label="Toggle navigation">
<span class="navbar-toggler-icon"></span>
</button>
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">Navbar</a>
<div class="collapse navbar-collapse" id="navbarNav">
<ul class="navbar-nav">
<li class="nav-item active">
<a class="nav-link" href="#">Home <span class="sr-only">(current)</span></a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#">Features</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#">Pricing</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link disabled" href="#">Disabled</a>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</nav>And considering that we utilize classes for our navs, you can stay clear of the list-based technique completely if you wish.
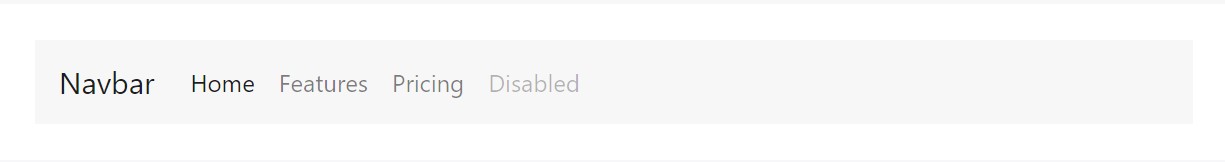
<nav class="navbar navbar-toggleable-md navbar-light bg-faded">
<button class="navbar-toggler navbar-toggler-right" type="button" data-toggle="collapse" data-target="#navbarNavAltMarkup" aria-controls="navbarNavAltMarkup" aria-expanded="false" aria-label="Toggle navigation">
<span class="navbar-toggler-icon"></span>
</button>
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">Navbar</a>
<div class="collapse navbar-collapse" id="navbarNavAltMarkup">
<div class="navbar-nav">
<a class="nav-item nav-link active" href="#">Home <span class="sr-only">(current)</span></a>
<a class="nav-item nav-link" href="#">Features</a>
<a class="nav-item nav-link" href="#">Pricing</a>
<a class="nav-item nav-link disabled" href="#">Disabled</a>
</div>
</div>
</nav>You can in addition apply dropdowns in your navbar nav. Dropdown menus demand a covering element for positioning, thus be sure to apply different and nested elements for .nav-item and .nav-link as shown below.
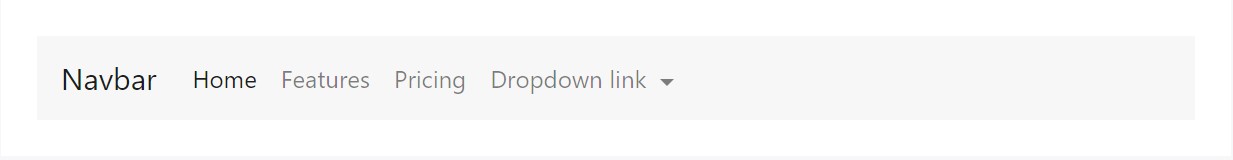
<nav class="navbar navbar-toggleable-md navbar-light bg-faded">
<button class="navbar-toggler navbar-toggler-right" type="button" data-toggle="collapse" data-target="#navbarNavDropdown" aria-controls="navbarNavDropdown" aria-expanded="false" aria-label="Toggle navigation">
<span class="navbar-toggler-icon"></span>
</button>
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">Navbar</a>
<div class="collapse navbar-collapse" id="navbarNavDropdown">
<ul class="navbar-nav">
<li class="nav-item active">
<a class="nav-link" href="#">Home <span class="sr-only">(current)</span></a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#">Features</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#">Pricing</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item dropdown">
<a class="nav-link dropdown-toggle" href="http://example.com" id="navbarDropdownMenuLink" data-toggle="dropdown" aria-haspopup="true" aria-expanded="false">
Dropdown link
</a>
<div class="dropdown-menu" aria-labelledby="navbarDropdownMenuLink">
<a class="dropdown-item" href="#">Action</a>
<a class="dropdown-item" href="#">Another action</a>
<a class="dropdown-item" href="#">Something else here</a>
</div>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</nav>Forms
Insert various form controls and elements within a navbar by using .form-inline.

<nav class="navbar navbar-light bg-faded">
<form class="form-inline">
<input class="form-control mr-sm-2" type="text" placeholder="Search">
<button class="btn btn-outline-success my-2 my-sm-0" type="submit">Search</button>
</form>
</nav>Straighten the contents of your inline forms along with utilities as needed.
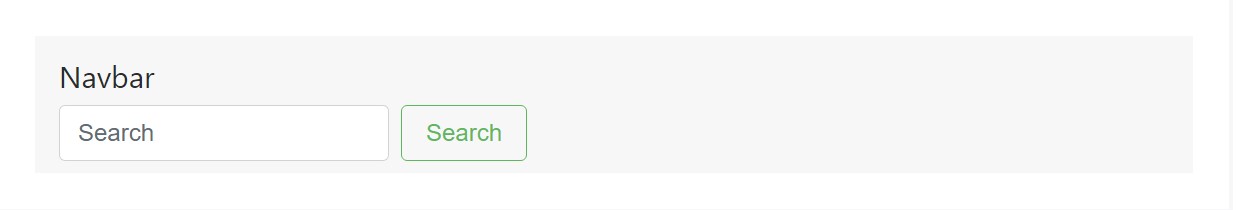
<nav class="navbar navbar-light bg-faded justify-content-between">
<a class="navbar-brand">Navbar</a>
<form class="form-inline">
<input class="form-control mr-sm-2" type="text" placeholder="Search">
<button class="btn btn-outline-success my-2 my-sm-0" type="submit">Search</button>
</form>
</nav>Input groups operate, too:

<nav class="navbar navbar-light bg-faded">
<form class="form-inline">
<div class="input-group">
<span class="input-group-addon" id="basic-addon1">@</span>
<input type="text" class="form-control" placeholder="Username" aria-describedby="basic-addon1">
</div>
</form>
</nav>Various buttons are supported as component of these navbar forms, too. This is in addition a fantastic reminder that vertical positioning utilities may be utilized to adjust several sized elements.

<nav class="navbar navbar-light bg-faded">
<form class="form-inline">
<button class="btn btn-outline-success" type="button">Main button</button>
<button class="btn btn-sm align-middle btn-outline-secondary" type="button">Smaller button</button>
</form>
</nav>Text
Navbars may possibly include bits of text message by using .navbar-text. This specific class changes vertical position and horizontal spacing for strings of text message.

<nav class="navbar navbar-light bg-faded">
<span class="navbar-text">
Navbar text with an inline element
</span>
</nav>Mix up and match with different elements and utilities as wanted.
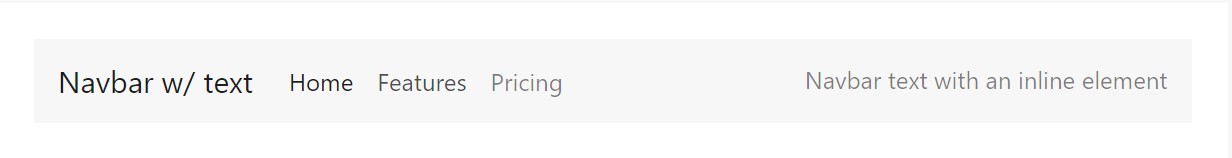
<nav class="navbar navbar-toggleable-md navbar-light bg-faded">
<button class="navbar-toggler navbar-toggler-right" type="button" data-toggle="collapse" data-target="#navbarText" aria-controls="navbarText" aria-expanded="false" aria-label="Toggle navigation">
<span class="navbar-toggler-icon"></span>
</button>
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">Navbar w/ text</a>
<div class="collapse navbar-collapse" id="navbarText">
<ul class="navbar-nav mr-auto">
<li class="nav-item active">
<a class="nav-link" href="#">Home <span class="sr-only">(current)</span></a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#">Features</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#">Pricing</a>
</li>
</ul>
<span class="navbar-text">
Navbar text with an inline element
</span>
</div>
</nav>Coloration
Theming the navbar has certainly never been actually simpler thanks to the mixture of style classes and background-color utilities. Select from .navbar-light for usage with light background color tones , or .navbar-inverse for dark background color options. After that, modify with .bg-* utilities.
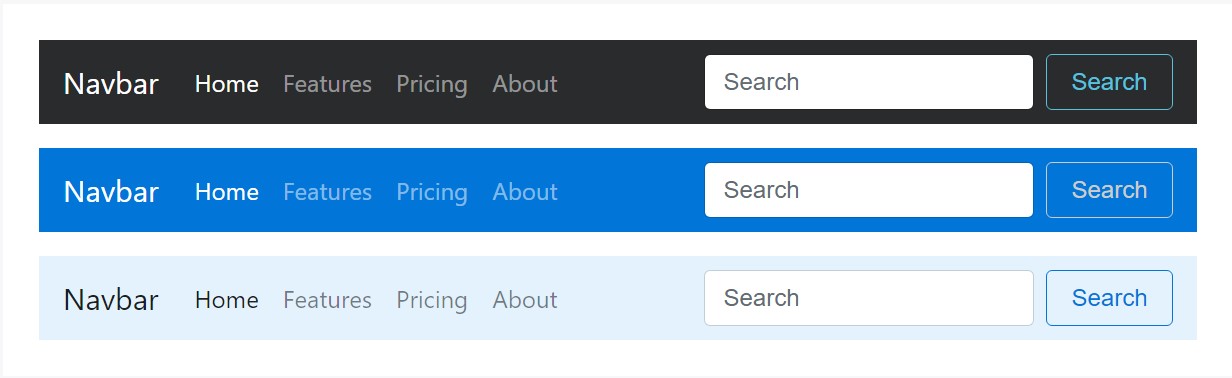
<nav class="navbar navbar-inverse bg-inverse">
<!-- Navbar content -->
</nav>
<nav class="navbar navbar-inverse bg-primary">
<!-- Navbar content -->
</nav>
<nav class="navbar navbar-light" style="background-color: #e3f2fd;">
<!-- Navbar content -->
</nav>Containers
Despite the fact it is simply not demanded, you can surely cover a navbar in a .container to focus it on a webpage or add one just within to simply centralize the elements of a corrected or else fixed top navbar.

<div class="container">
<nav class="navbar navbar-toggleable-md navbar-light bg-faded">
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">Navbar</a>
</nav>
</div>When the container is in your navbar, its horizontal padding is cleared away at breakpoints below your determined
.navbar-toggleable-* class. This guarantees we're not doubling up on padding needlessly on lower viewports whenever your navbar is collapsed.

<nav class="navbar navbar-toggleable-md navbar-light bg-faded">
<div class="container">
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">Navbar</a>
</div>
</nav>Arrangement
Use placement utilities to place navbars in non-static placements. Choose positioned to the top, positioned to the bottom, or else stickied to the top . Keep in mind that position: sticky, utilized for .sticky-top, actually isn't completely supported in each browser.

<nav class="navbar navbar-light bg-faded">
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">Full width</a>
</nav>
<nav class="navbar fixed-top navbar-light bg-faded">
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">Fixed top</a>
</nav>
<nav class="navbar fixed-bottom navbar-light bg-faded">
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">Fixed bottom</a>
</nav>
<nav class="navbar sticky-top navbar-light bg-faded">
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">Sticky top</a>
</nav>Responsive tendencies
Navbars can easily work with .navbar-toggler, .navbar-collapse, and .navbar-toggleable-* classes to alter anytime their web content collapses behind a button . In combination with other utilities, you are able to simply choose when to show or conceal particular features.
Toggler
Navbar togglers can possibly be left or right aligned with .navbar-toggler-left or .navbar-toggler-right modifiers. These are completely set up inside of the navbar to stay away from intrusion with the collapsed state. You are able to in addition apply your personal formats to arrange togglers. Listed here are examples of different toggle designs.
By having no .navbar-brand revealed in lowest breakpoint:

<nav class="navbar navbar-toggleable-md navbar-light bg-faded">
<button class="navbar-toggler" type="button" data-toggle="collapse" data-target="#navbarTogglerDemo01" aria-controls="navbarTogglerDemo01" aria-expanded="false" aria-label="Toggle navigation">
<span class="navbar-toggler-icon"></span>
</button>
<div class="collapse navbar-collapse" id="navbarTogglerDemo01">
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">Hidden brand</a>
<ul class="navbar-nav mr-auto mt-2 mt-lg-0">
<li class="nav-item active">
<a class="nav-link" href="#">Home <span class="sr-only">(current)</span></a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#">Link</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link disabled" href="#">Disabled</a>
</li>
</ul>
<form class="form-inline my-2 my-lg-0">
<input class="form-control mr-sm-2" type="text" placeholder="Search">
<button class="btn btn-outline-success my-2 my-sm-0" type="submit">Search</button>
</form>
</div>
</nav>Along with a brand name revealed on the left and toggler on the right:

<nav class="navbar navbar-toggleable-md navbar-light bg-faded">
<button class="navbar-toggler navbar-toggler-right" type="button" data-toggle="collapse" data-target="#navbarTogglerDemo02" aria-controls="navbarTogglerDemo02" aria-expanded="false" aria-label="Toggle navigation">
<span class="navbar-toggler-icon"></span>
</button>
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">Navbar</a>
<div class="collapse navbar-collapse" id="navbarTogglerDemo02">
<ul class="navbar-nav mr-auto mt-2 mt-md-0">
<li class="nav-item active">
<a class="nav-link" href="#">Home <span class="sr-only">(current)</span></a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="#">Link</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link disabled" href="#">Disabled</a>
</li>
</ul>
<form class="form-inline my-2 my-lg-0">
<input class="form-control mr-sm-2" type="text" placeholder="Search">
<button class="btn btn-outline-success my-2 my-sm-0" type="submit">Search</button>
</form>
</div>
</nav>Alternative web content
In some cases you wish to utilize the collapse plugin in order to cause covert web content elsewhere on the web page. Because plugin works with the id and data-target matching, that is really effortlessly performed!

<div class="pos-f-t">
<div class="collapse" id="navbarToggleExternalContent">
<div class="bg-inverse p-4">
<h4 class="text-white">Collapsed content</h4>
<span class="text-muted">Toggleable via the navbar brand.</span>
</div>
</div>
<nav class="navbar navbar-inverse bg-inverse">
<button class="navbar-toggler" type="button" data-toggle="collapse" data-target="#navbarToggleExternalContent" aria-controls="navbarToggleExternalContent" aria-expanded="false" aria-label="Toggle navigation">
<span class="navbar-toggler-icon"></span>
</button>
</nav>
</div>Conclusions
Thus essentially these are the way a navbar need to be constructed in Bootstrap 4 and the new neat changes coming with the newest version. All that's left for you is considering cool page system and content.
Check out a couple of video information regarding Bootstrap Navbar:
Related topics:
Bootstrap Navbar main documentation
Align navbar thing to the right within Bootstrap 4 alpha 6
Bootstrap Responsive menu in Mobirise
CSS3 Bootstrap Navigation Menu Templates
HTML5 Bootstrap Toggle Menu Examples